
Flex 入门到精通教程
一、Flex 布局是什么?
-
Flex 是 Flexible Box 的缩写,意为"弹性布局",用来为盒状模型提供最大的灵活性。
-
任何一个容器都可以指定为 Flex 布局。
.box {
display: flex;
}行内元素也可以使用 Flex 布局。
.box {
display: inline-flex;
}Webkit 内核的浏览器,必须加上-webkit 前缀。
.box {
display: -webkit-flex; /* Safari */
display: flex;
}注意
设为 Flex 布局以后,子元素的 float、clear 和 vertical-align 属性将失效。
二、基本概念
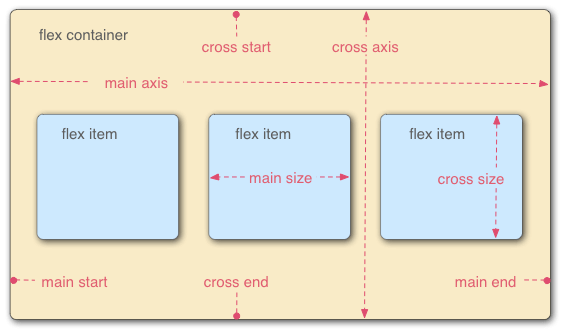
采用 Flex 布局的元素,称为 Flex 容器(flex container),简称"容器"。它的所有子元素自动成为容器成员,称为 Flex 项目(flex item),简称"项目"。
-
容器默认存在两根轴:水平的主轴(main axis)和垂直的交叉轴(cross axis)。主轴的开始位置(与边框的交叉点)叫做 main start,结束位置叫做 main end;交叉轴的开始位置叫做 cross start,结束位置叫做 cross end。
-
项目默认沿主轴排列。单个项目占据的主轴空间叫做 main size,占据的交叉轴空间叫做 cross size。
三、容器的属性
以下 6 个属性设置在容器上。
-
flex-direction
-
flex-wrap
-
flex-flow
-
justify-content
-
align-items
-
align-content
3.1 flex-direction 属性
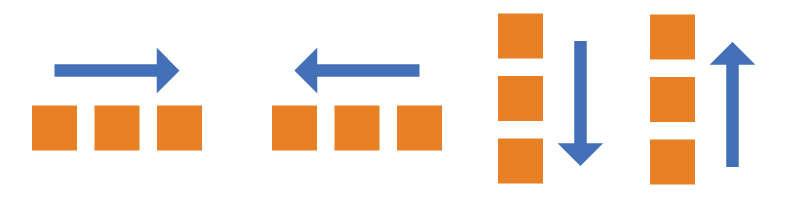
flex-direction 属性决定主轴的方向(即项目的排列方向)。
.box {
flex-direction: row | row-reverse | column | column-reverse;
}
-
row(默认值):主轴为水平方向,起点在左端。
-
row-reverse:主轴为水平方向,起点在右端。
-
column:主轴为垂直方向,起点在上沿。
-
column-reverse:主轴为垂直方向,起点在下沿。
3.2 flex-wrap 属性
默认情况下,项目都排在一条线(又称"轴线")上。flex-wrap 属性定义,如果一条轴线排不下,如何换行。
.box {
flex-wrap: nowrap | wrap | wrap-reverse;
}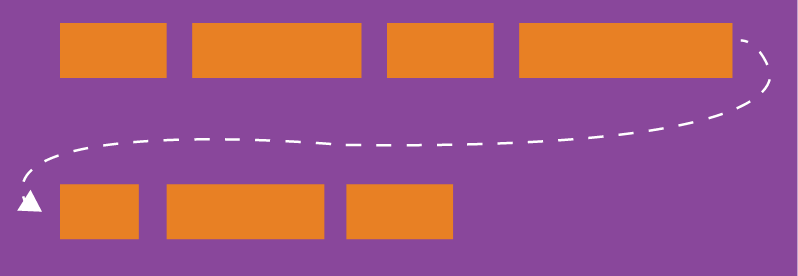
(1)nowrap(默认):不换行。
(2)wrap:换行,第一行在上方。

(3)wrap-reverse:换行,第一行在下方。

3.3 flex-flow
flex-flow 属性是 flex-direction 属性和 flex-wrap 属性的简写形式,默认值为 row nowrap。
.box {
flex-flow: <flex-direction> || <flex-wrap>;
}3.4 justify-content 属性
justify-content 属性定义了项目在主轴上的对齐方式。
.box {
justify-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around;
}
-
flex-start(默认值):左对齐
-
flex-end:右对齐
-
center: 居中
-
space-between:两端对齐,项目之间的间隔都相等。
-
space-around:每个项目两侧的间隔相等。所以,项目之间的间隔比项目与边框的间隔大一倍。
3.5 align-items 属性
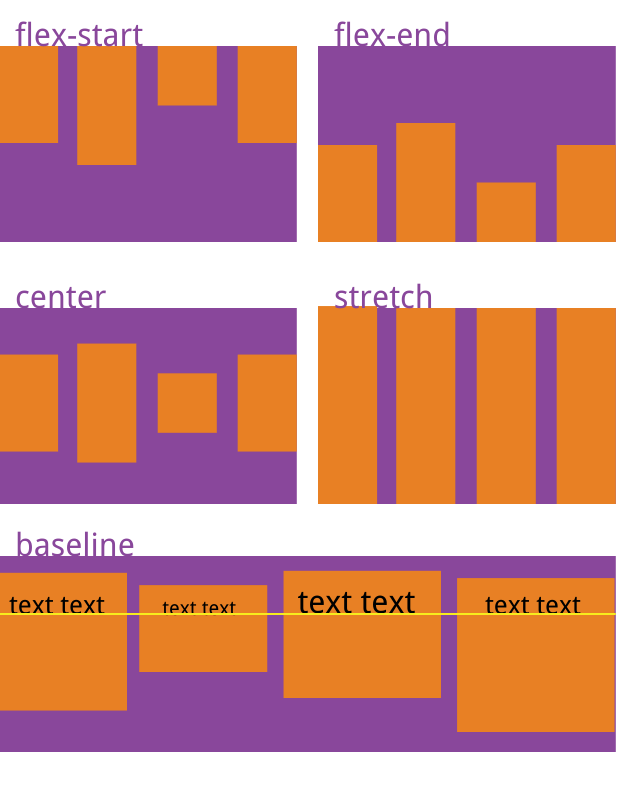
align-items 属性定义项目在交叉轴上如何对齐。
.box {
align-items: flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch;
}
-
flex-start:交叉轴的起点对齐。
-
flex-end:交叉轴的终点对齐。
-
center:交叉轴的中点对齐。
-
baseline: 项目的第一行文字的基线对齐。
-
stretch(默认值):如果项目未设置高度或设为 auto,将占满整个容器的高度。
3.6 align-content 属性
align-content 属性定义了多根轴线的对齐方式。如果项目只有一根轴线,该属性不起作用。
.box {
align-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around |
stretch;
}
-
flex-start:与交叉轴的起点对齐。
-
flex-end:与交叉轴的终点对齐。
-
center:与交叉轴的中点对齐。
-
space-between:与交叉轴两端对齐,轴线之间的间隔平均分布。
-
space-around:每根轴线两侧的间隔都相等。所以,轴线之间的间隔比轴线与边框的间隔大一倍。
-
stretch(默认值):轴线占满整个交叉轴。
四、项目的属性
-
order
-
flex-grow
-
flex-shrink
-
flex-basis
-
flex
-
align-self
4.1 order 属性
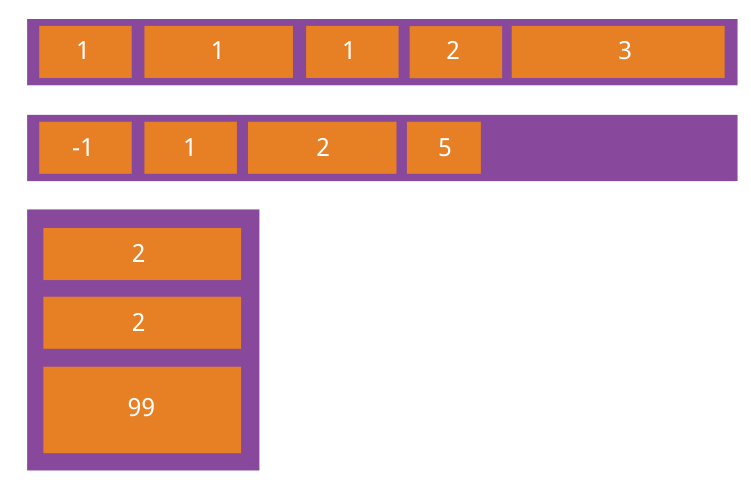
order 属性定义项目的排列顺序。数值越小,排列越靠前,默认为 0。
.item {
order: <integer>;
}
4.2 flex-grow 属性
flex-grow 属性定义项目的放大比例,默认为 0,即如果存在剩余空间,也不放大。
.item {
flex-grow: <number>; /* default 0 */
}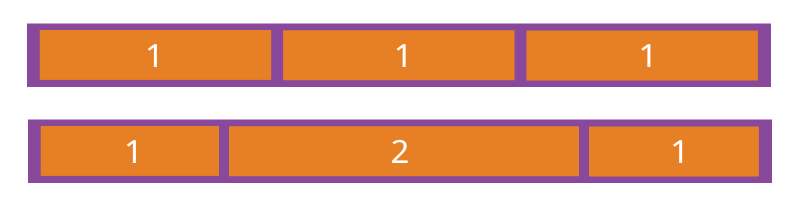
如果所有项目的 flex-grow 属性都为 1,则它们将等分剩余空间(如果有的话)。如果一个项目的 flex-grow 属性为 2,其他项目都为 1,则前者占据的剩余空间将比其他项多一倍。
4.3 flex-shrink 属性
flex-shrink 属性定义了项目的缩小比例,默认为 1,即如果空间不足,该项目将缩小。
.item {
flex-shrink: <number>; /* default 1 */
}
如果所有项目的 flex-shrink 属性都为 1,当空间不足时,都将等比例缩小。如果一个项目的 flex-shrink 属性为 0,其他项目都为 1,则空间不足时,前者不缩小。
负值对该属性无效。
4.4 flex-basis 属性
flex-basis 属性定义了在分配多余空间之前,项目占据的主轴空间(main size)。浏览器根据这个属性,计算主轴是否有多余空间。它的默认值为 auto,即项目的本来大小。
.item {
flex-basis: <length> | auto; /* default auto */
}它可以设为跟 width 或 height 属性一样的值(比如 350px),则项目将占据固定空间。
4.5 flex 属性
flex 属性是 flex-grow, flex-shrink 和 flex-basis 的简写,默认值为 0 1 auto。后两个属性可选。
.item {
flex: none | [ < "flex-grow" > < "flex-shrink" >? || < "flex-basis" > ];
}该属性有两个快捷值:auto (1 1 auto) 和 none (0 0 auto)。
建议优先使用这个属性,而不是单独写三个分离的属性,因为浏览器会推算相关值。
4.6 align-self 属性
align-self 属性允许单个项目有与其他项目不一样的对齐方式,可覆盖 align-items 属性。默认值为 auto,表示继承父元素的 align-items 属性,如果没有父元素,则等同于 stretch。
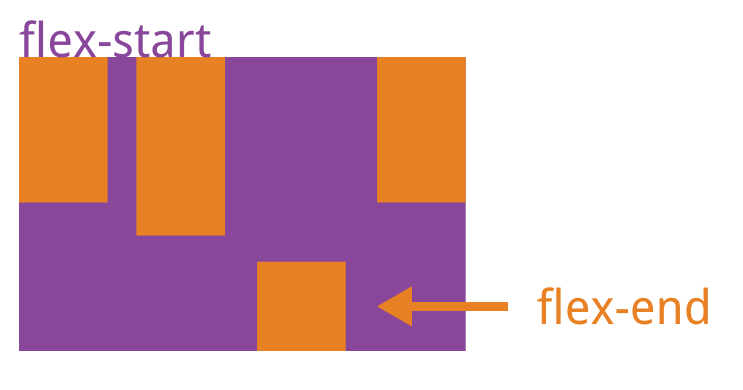
该属性可能取 6 个值,除了 auto,其他都与 align-items 属性完全一致。
实例篇
1.1 单项目
Flex 布局默认就是首行左对齐

.box {
display: flex;
}设置项目的对齐方式,就能实现居中对齐和右对齐。

.box {
display: flex;
//居中对齐
justify-content: center;
}
.box {
display: flex;
//右对齐
justify-content: flex-end;
}设置交叉轴对齐方式,可以垂直移动主轴。

.box {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
.box {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.box {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: flex-end;
}
.box {
display: flex;
justify-content: flex-end;
align-items: flex-end;
}1.2 双项目

.box {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
}
.box {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: space-between;
}
.box {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
}
.box {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: flex-end;
}
.box {
display: flex;
}
.item:nth-child(2) {
align-self: center;
}
.box {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
}
.item:nth-child(2) {
align-self: flex-end;
}1.3 三项目

.box {
display: flex;
}
.item:nth-child(2) {
align-self: center;
}
.item:nth-child(3) {
align-self: flex-end;
}1.4 四项目

.box {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
justify-content: flex-end;
align-content: space-between;
}
<div class="box">
<div class="column">
<span class="item"></span>
<span class="item"></span>
</div>
<div class="column">
<span class="item"></span>
<span class="item"></span>
</div>
</div>.box {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
align-content: space-between;
}
.column {
flex-basis: 100%;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
}1.5 六项目

.box {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
align-content: space-between;
}
.box {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
flex-wrap: wrap;
align-content: space-between;
}
HTML 代码如下。
<div class="box">
<div class="row">
<span class="item"></span>
<span class="item"></span>
<span class="item"></span>
</div>
<div class="row">
<span class="item"></span>
</div>
<div class="row">
<span class="item"></span>
<span class="item"></span>
</div>
</div>CSS 代码如下。
.box {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
.row {
flex-basis: 100%;
display: flex;
}
.row:nth-child(2) {
justify-content: center;
}
.row:nth-child(3) {
justify-content: space-between;
}1.6 九项目

.box {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}二、网格布局
2.1 基本网格布局
最简单的网格布局,就是平均分布。在容器里面平均分配空间,跟上面的骰子布局很像,但是需要设置项目的自动缩放。

HTML 代码如下。
html<div class="Grid"> <div class="Grid-cell">...</div> <div class="Grid-cell">...</div> <div class="Grid-cell">...</div> </div>
CSS 代码如下。
css.Grid { display: flex; } .Grid-cell { flex: 1; }
2.2 百分比布局
某个网格的宽度为固定的百分比,其余网格平均分配剩余的空间。

HTML 代码如下。
<div class="Grid">
<div class="Grid-cell u-1of4">...</div>
<div class="Grid-cell">...</div>
<div class="Grid-cell u-1of3">...</div>
</div>.Grid {
display: flex;
}
.Grid-cell {
flex: 1;
}
.Grid-cell.u-full {
flex: 0 0 100%;
}
.Grid-cell.u-1of2 {
flex: 0 0 50%;
}
.Grid-cell.u-1of3 {
flex: 0 0 33.3333%;
}
.Grid-cell.u-1of4 {
flex: 0 0 25%;
}三、圣杯布局
圣杯布局(Holy Grail Layout)指的是一种最常见的网站布局。页面从上到下,分成三个部分:头部(header),躯干(body),尾部(footer)。其中躯干又水平分成三栏,从左到右为:导航、主栏、副栏。

<body class="HolyGrail">
<header>...</header>
<div class="HolyGrail-body">
<main class="HolyGrail-content">...</main>
<nav class="HolyGrail-nav">...</nav>
<aside class="HolyGrail-ads">...</aside>
</div>
<footer>...</footer>
</body>.HolyGrail {
display: flex;
min-height: 100vh;
flex-direction: column;
}
header,
footer {
flex: 1;
}
.HolyGrail-body {
display: flex;
flex: 1;
}
.HolyGrail-content {
flex: 1;
}
.HolyGrail-nav,
.HolyGrail-ads {
/* 两个边栏的宽度设为12em */
flex: 0 0 12em;
}
.HolyGrail-nav {
/* 导航放到最左边 */
order: -1;
}如果是小屏幕,躯干的三栏自动变为垂直叠加。
@media (max-width: 768px) {
.HolyGrail-body {
flex-direction: column;
flex: 1;
}
.HolyGrail-nav,
.HolyGrail-ads,
.HolyGrail-content {
flex: auto;
}
}四、输入框的布局
我们常常需要在输入框的前方添加提示,后方添加按钮。

<div class="InputAddOn">
<span class="InputAddOn-item">...</span>
<input class="InputAddOn-field" />
<button class="InputAddOn-item">...</button>
</div>.InputAddOn {
display: flex;
}
.InputAddOn-field {
flex: 1;
}五、悬挂式布局
有时,主栏的左侧或右侧,需要添加一个图片栏。

<div class="Media">
<img class="Media-figure" src="" alt="" />
<p class="Media-body">...</p>
</div>.Media {
display: flex;
align-items: flex-start;
}
.Media-figure {
margin-right: 1em;
}
.Media-body {
flex: 1;
}六、固定的底栏
有时,页面内容太少,无法占满一屏的高度,底栏就会抬高到页面的中间。这时可以采用 Flex 布局,让底栏总是出现在页面的底部。

<body class="Site">
<header>...</header>
<main class="Site-content">...</main>
<footer>...</footer>
</body>.Site {
display: flex;
min-height: 100vh;
flex-direction: column;
}
.Site-content {
flex: 1;
}七,流式布局
每行的项目数固定,会自动分行。

.parent {
width: 200px;
height: 150px;
background-color: black;
display: flex;
flex-flow: row wrap;
align-content: flex-start;
}
.child {
box-sizing: border-box;
background-color: white;
flex: 0 0 25%;
height: 50px;
border: 1px solid red;
}